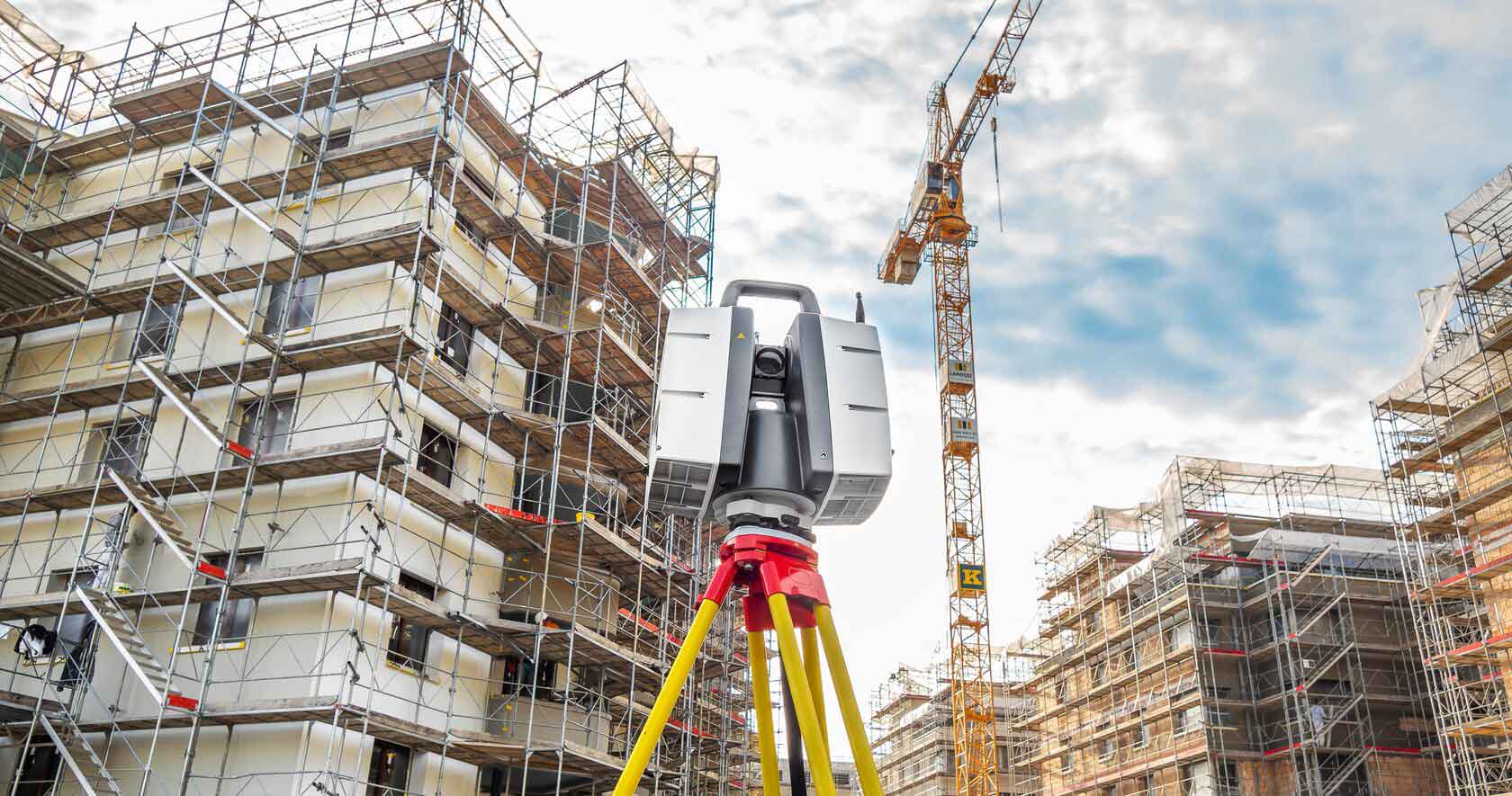
There are different 3D scanning methods, but today, we will focus on 3D laser scanners. Most industrial 3D scanners work on the principle of laser triangulation. The principles of triangulation gather data points in a reference plane established by a laser fan beam. All data points will be somewhere on this plane. By examining where the laser is seen by the sensor, the scanner can calculate the distance to the object. Thus, 3D laser scanners can measure fine details and capture free-form shapes to generate highly accurate point clouds.
3D Laser scanning in construction
3D laser scanning, also known as high-definition surveying or reality capture, is not a new technology at all. The technology’s roots date back to the 1960s. However, it was not until the 1990s that it began being used for design and engineering purposes. Today, laser scanning has become commonplace, now moving into a variety of markets, including construction.
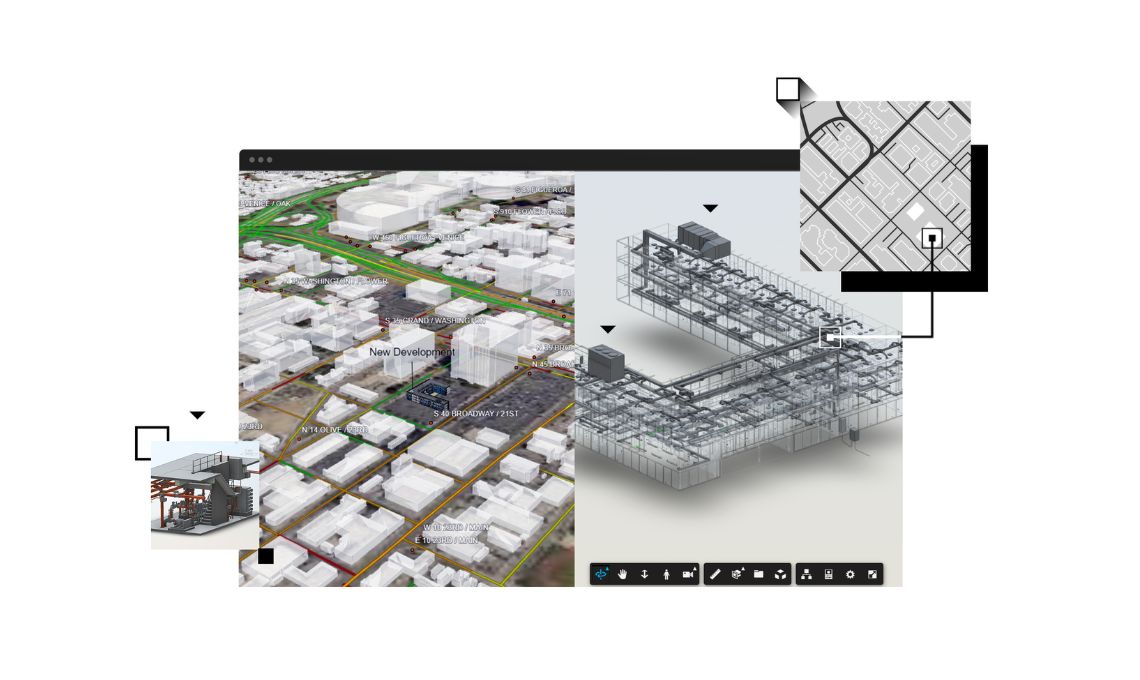
On a construction site, laser scanning is used to capture detailed data. A laser beam assesses the structure’s numerous dimensions, including the length, width, and height of the building components, as well as their connections to one another. The data it provides to construction professionals is known as point cloud. That is, a database connecting points in a 3D coordinate system.
Why construction professionals should use 3D laser scanners
In particular, laser scanning is a starting point, sometimes even before BIM when it comes to site design. Today, many professionals are adopting a “scan-to-BIM” design approach to capture detailed information to start and manage the process from the beginning. In addition, if we need to gain an accurate insight into the project’s current state, 3D scanning also provides access to the information you need on-demand. Taking into account that each scanned version of the building remains on record, contractors can quickly compare previous versions of the building to the current one. Thus, whether we are working on building renovations or new construction, 3D laser scanners allow designers and other construction professionals to ensure project accuracy by measuring progress against the original design. This process ensures that there is an accurate record to refer to during every phase of the construction cycle.
A major benefit of laser scanning is when it comes to construction coordination, specifically in avoiding clashes between different systems (i.e., electrical, plumbing). 3D scanning can be done throughout various phases of a construction project to better document milestones, reduce the necessity of change orders, and pass off work to other professionals. In this way, laser scanning in buildings can also help document where mistakes were made and identify solutions more quickly.
It’s no secret that reworks are one of the most significant obstacles in construction. Having to reinstall specific components because of a mistake generates additional work, supply costs, and prolongs the project as a whole. Thanks to the use of 3D lasers, general contractors can reduce rework by verifying construction accuracy during the building phase. While that may not seem significant, 1-3% of a multi-million dollar construction project is a significant amount of money, which makes laser scanning and the costs associated worthy of consideration.
It should be noted that for complex engineering projects, dedicated machines are typically required to use lasers and precise global positioning. We at MicroCAD offer Leica laser scanners as the perfect partner for any tasks in 3D laser scanning. We utilize industry-leading HDS instrumentation and software from Leica Geosystems, delivering outstanding range, speed, and highest quality 3D data.